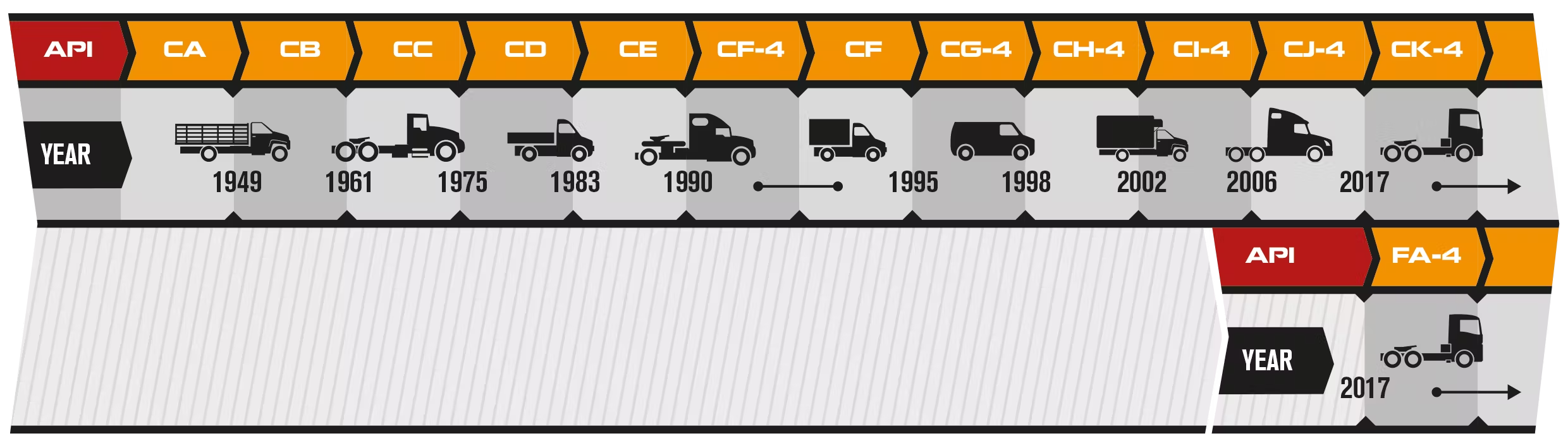
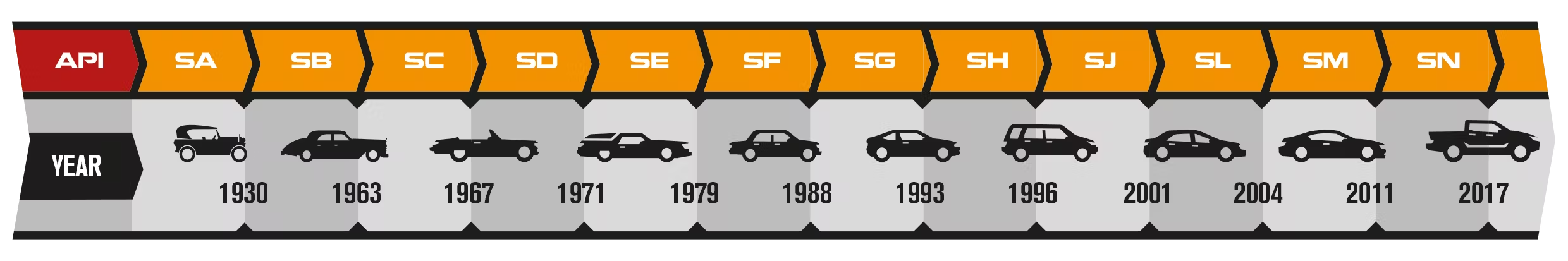
The API (American Petroleum Institute) motor oil classification system dates back to 1969. Its main purpose is to classify motor oils by quality and the equipment used.

According to these categories, the names of the corresponding standards use the necessary designations. For example, oils standardized in this way are usually named API SE. Now we will examine in more detail what these letters mean.
For each new class, an additional letter is assigned in the alphabet. Universal oils for gasoline and diesel engines are designated by two symbols of the corresponding categories: the first symbol is the main one (indicates which engine the oil is for), and the second one indicates the possibility of using the year of engine production, and whether it has a turbine or not.
S (Service) - consists of quality categories of motor oils for gasoline engines, listed in chronological order.
C (Commercial) - consists of quality and purpose categories of oils for diesel engines, listed in chronological order.
If the oil meets several standards, for example, API SJ/CF, it means it is suitable for both gasoline and diesel engines of this category. The figure below shows all the main oil standards in the API category.
Based on these two tables, we will tell you about the most popular categories today.
Gasoline oils
SJ — The category was approved on 06.11.1995, licenses began to be issued on 15.10.1996. Automotive oils of this category are intended for all currently used gasoline engines and completely replace oils of all previously existing categories in older engine models. Maximum level of performance properties. Possibility of certification according to the API SJ/EC energy saving category.
SL — introduced in July 2001 for multi-valve turbocharged engines equipped with exhaust control and neutralization systems. API SL implies the following improvements in motor oils:
- reduced exhaust toxicity
- protection of exhaust control and neutralization systems
- increased wear protection
- enhanced protection against high temperature deposits
- extended replacement interval
SM — was put into effect in November 2004. API SM includes motor oils for gasoline engines manufactured after 2004. Motor oils that meet the requirements will provide reliable lubrication for turbocharged and multi-valve engines. Motor oil certified according to the API SM classification may have an additional specification ILSAC GF-4, which indicates high energy-saving properties of the motor oil.
SN — was put into effect in October 2010. Today, these are the latest (and therefore the most stringent) requirements that are imposed on manufacturers of motor oils for gasoline engines. Certified oils imply the possibility of use in all gasoline engines of the current generation (manufactured after 2010).
Important in the emergence of the API SN API classification class is the introduction of the following requirements
- Can be used in engines using biofuels;
- All oils of the standard are energy-saving;
- Increased requirements for ensuring engine wear resistance;
Diesel oils
CF — introduced in 1994. Oils for off-road equipment, engines with separating injection, including those running on fuel with a sulfur content of 0.5% by weight and higher. Replaces CD oils.
CF-2 — introduced in 1994. Improved performance, used instead of CD-II for two-stroke engines. The highest oil for two-stroke engines.
CF-4 — introduced in 1990. For high-speed four-stroke diesel engines with and without turbocharging. Can be used instead of CD and CE oils. Highest for four-stroke engines.
CG-4 — introduced in 1995. For engines of high-speed diesel equipment running on fuel with a sulfur content of less than 0.5%. CG-4 oils for engines that meet the exhaust gas toxicity requirements introduced in the USA since 1994. Replaces CD, CE and CF-4 category oils. Highest for models since 1995.
CH-4 — introduced in 1998. For high-speed four-stroke engines that meet the exhaust toxicity requirements introduced in the USA since 1998. CH-4 oils allow the use of fuel with a sulfur content of up to 0.5% by weight. Can be used instead of CD, CE, CF-4 and CG-4 oils.
CI-4 — introduced in 2002. For high-speed four-stroke engines designed to meet exhaust gas toxicity standards implemented in 2002. CI-4 oils allow the use of fuel with a sulfur content of up to 0.5% by weight, and are also used in engines with an exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) system. Replaces CD, CE, CF-4, CG 4 and CH-4 oils. In 2004, an additional category API CI-4 PLUS was introduced. The requirements for soot formation, deposits, and viscosity indices have been tightened.
CJ-4 — Introduced in 2006. For high-speed, four-stroke engines designed to meet 2007 on-highway emission standards. CJ-4 oils are approved for use with fuels containing up to 500 ppm (0.05% by weight) of sulfur. However, use with fuels containing more than 15 ppm (0.0015% by weight) of sulfur may affect the performance of exhaust gas treatment systems and/or oil drain intervals. CJ-4 oils are recommended for engines equipped with diesel particulate filters and other exhaust gas treatment systems.